Core Components
The NextJudge framework is composed of a number of components. These components allow us to encapsulate functionality and make the framework more modular.
NextJudge follows a distributed architecture composed of a number of components/microservices that communicate with each other via HTTP and message queues (RabbitMQ).
The following diagram shows the current architecture of NextJudge:
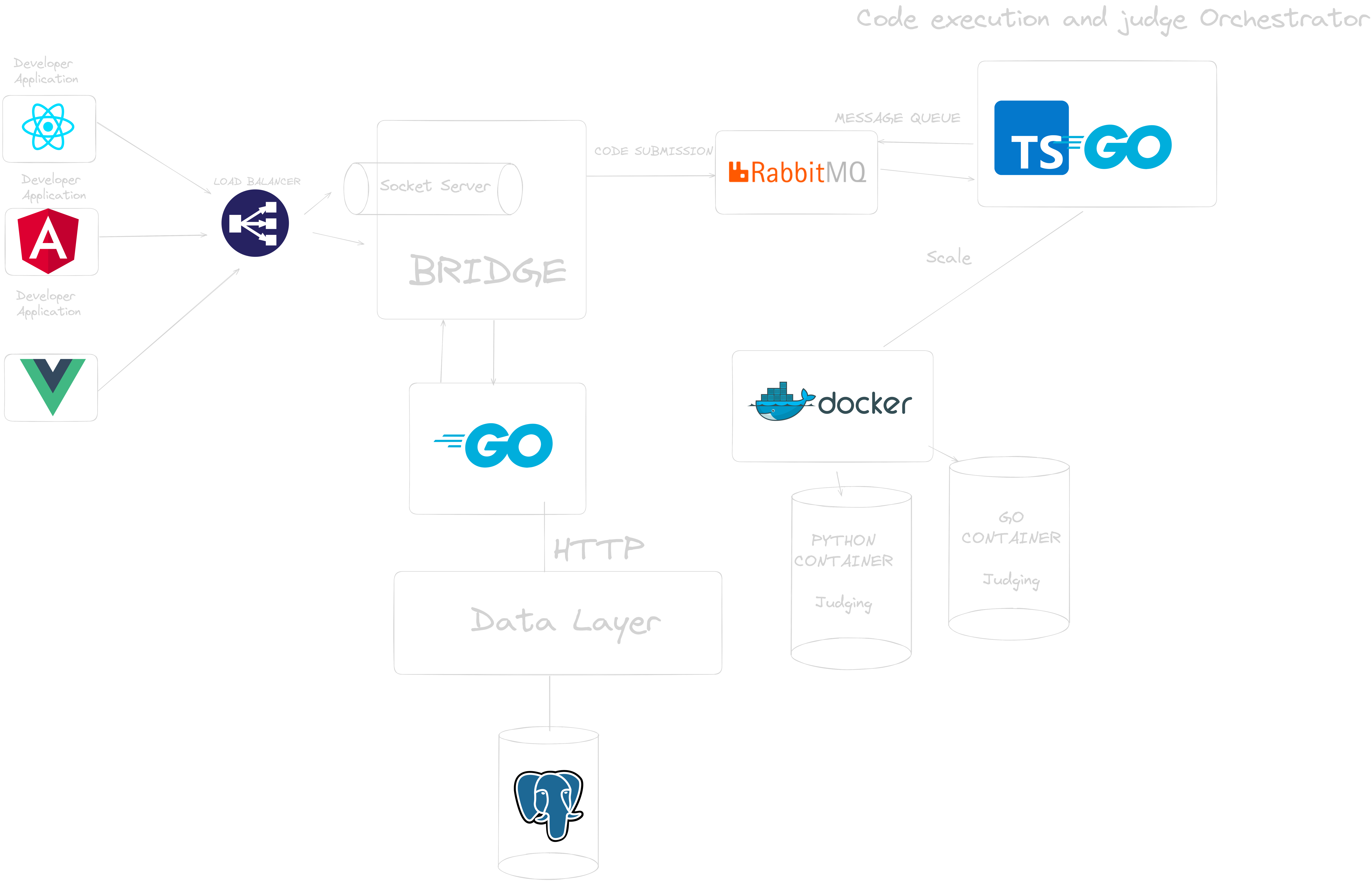
Components
Section titled “Components”Web Client
Section titled “Web Client”The Web Application is a Next.js-based full-stack application that provides the user interface for NextJudge. It handles user authentication, problem browsing, code submission, contest management, and real-time updates.
Technologies:
- Next.js 14+ (React framework)
- TypeScript
- TailwindCSS
- NextAuth for authentication
- Monaco Editor for code editing
Key Features:
- User authentication and authorization
- Problem browsing and filtering
- Code editor with syntax highlighting
- Real-time submission status updates
- Contest management interface
- Leaderboard display
- Admin dashboard
Data Layer
Section titled “Data Layer”The Data Layer is a Go-based REST API service that acts as the central data store and business logic layer for NextJudge. It manages all persistent data including users, problems, submissions, contests (events), and languages.
Technologies:
- Go (Golang)
- PostgreSQL database
- GORM for database ORM
- RabbitMQ for message queuing
- Elasticsearch (optional) for search functionality
- JWT for authentication
Key Responsibilities:
- User management and authentication
- Problem and test case storage
- Submission tracking and status management
- Contest (event) management
- Language configuration
- API endpoint exposure for all data operations
API Endpoints:
/v1/users- User management/v1/problems- Problem management/v1/submissions- Submission tracking/v1/events- Contest management/v1/languages- Language configuration/v1/input_submissions- Custom input execution
Judge Service
Section titled “Judge Service”The Judge service is responsible for compiling and executing code submissions in a secure, isolated environment. It receives submission requests from RabbitMQ, compiles the code, runs it against test cases, and returns the results.
Technologies:
- Python 3
- nsjail for process isolation
- RabbitMQ for message queuing
- Docker for isolation
Key Responsibilities:
- Code compilation for multiple languages
- Secure execution in isolated environments
- Test case execution and comparison
- Resource limit enforcement (time, memory, CPU)
- Result reporting back to the data layer
Security Features:
- nsjail sandboxing for process isolation
- Resource limits (CPU time, memory, file descriptors)
- Network access restrictions
- File system restrictions
- User namespace isolation
Supported Languages:
The judge supports multiple programming languages including C, C++, Python, Java, JavaScript, TypeScript, Go, Rust, Ruby, Lua, Kotlin, and Haskell. Language configurations are defined in languages.toml.
Message Queue (RabbitMQ)
Section titled “Message Queue (RabbitMQ)”RabbitMQ serves as the communication layer between the data layer and judge services. It handles asynchronous submission processing, allowing the system to scale horizontally by adding multiple judge instances.
Key Features:
- Submission queue for pending submissions
- RPC-style communication for judge-data layer interaction
- Message durability and reliability
- Horizontal scaling support
Database (PostgreSQL)
Section titled “Database (PostgreSQL)”PostgreSQL stores all persistent data for the NextJudge platform, including:
- User accounts and authentication data
- Problem descriptions and metadata
- Test cases (input/output pairs)
- Submission records and results
- Contest (event) information
- Language configurations
- Categories and problem classifications
CLI Tool
Section titled “CLI Tool”The NextJudge CLI provides a command-line interface for interacting with the platform, allowing developers to work with problems and submissions from their terminal.
Features:
- Download problem prompts and test cases
- Submit solutions from local files
- Test solutions locally using Docker
- Track current problem context
Usage:
nextjudge get <problem_id> # Download problemnextjudge submit solution.py # Submit solutionnextjudge test solution.rs # Test locallyCommunication Flow
Section titled “Communication Flow”- User Submission: User submits code through the web interface
- Data Layer: Receives submission, stores it in database, enqueues to RabbitMQ
- Judge Service: Picks up submission from queue, compiles and executes code
- Result Reporting: Judge sends results back to data layer via HTTP API
- Status Update: Data layer updates submission status, web interface polls for updates